Dogs perceive the world differently than humans. They have a unique set of sensory organs that allow them to experience the world in a way that is distinct from our own. One of the most important differences between how dogs and humans see the world is the way that they process visual information. Dogs have a filter over their eyes that helps them to see in low-light conditions. This filter also helps to protect their eyes from the sun's harmful rays.
The dog's visual filter is made up of a layer of cells called the tapetum lucidum. The tapetum lucidum is located behind the retina and it reflects light back into the eye. This helps to increase the amount of light that reaches the retina and it allows dogs to see better in low-light conditions. The tapetum lucidum also helps to protect the retina from damage caused by the sun's ultraviolet rays.
The dog's visual filter is an important part of their sensory system. It helps them to see in low-light conditions and it protects their eyes from damage. Without this filter, dogs would not be able to see as well in the dark and they would be more susceptible to eye damage.
Read also:Poppi Louiz Naked
How Dogs See the World
Dogs perceive the world differently than humans due to a unique filter over their eyes. This filter, composed of a layer of cells called the tapetum lucidum, enhances their vision in low-light conditions and protects their eyes from sun damage. Here are ten key aspects of this fascinating adaptation:
- Enhanced Night Vision
- Protection from UV Rays
- Increased Light Sensitivity
- Improved Depth Perception
- Motion Detection
- Color Perception
- Visual Field of View
- Binocular Vision
- Accommodation
- Tear Production
These aspects collectively contribute to a dog's unique visual experience. Their enhanced night vision allows them to navigate in darkness, while protection from UV rays safeguards their eyes from long-term damage. Increased light sensitivity and improved depth perception aid in hunting and obstacle avoidance. Motion detection and a wide field of view enhance their awareness of surroundings. Color perception, though different from humans, enables them to distinguish objects and communicate with each other. Binocular vision provides depth perception, and accommodation allows them to focus on objects at varying distances. Tear production lubricates their eyes and protects them from irritants.
Enhanced Night Vision
As part of the unique filter over their eyes, dogs possess enhanced night vision, enabling them to navigate and perceive their surroundings in low-light conditions. This remarkable ability stems from the presence of a reflective layer called the tapetum lucidum, located behind the retina. The tapetum lucidum reflects light back into the eye, increasing the amount of light available to the photoreceptors and enhancing the dog's ability to see in dim environments.
- Increased Light Sensitivity: The tapetum lucidum's reflective properties allow dogs to detect and utilize even faint sources of light, enhancing their visual acuity in low-light conditions.
- Improved Depth Perception: Enhanced night vision contributes to a dog's depth perception, enabling them to better gauge distances and navigate their surroundings in darkness.
- Enhanced Motion Detection: The increased light sensitivity and improved depth perception work together to enhance a dog's ability to detect and track moving objects in low-light conditions.
- Hunting and Predation: Enhanced night vision is particularly advantageous for dogs that hunt at dawn or dusk, allowing them to locate and pursue prey more effectively.
In summary, the enhanced night vision afforded by the tapetum lucidum is a crucial aspect of how dogs see the world filter. It empowers them to navigate, hunt, and interact with their environment effectively in low-light conditions, highlighting the remarkable adaptations that contribute to their unique sensory experiences.
Protection from UV Rays
The "how dogs see the world filter" includes protection from ultraviolet (UV) rays, a crucial aspect that safeguards their eyes from long-term damage. This protection stems from the unique anatomical features of their eyes, including the presence of a specialized structure called the tapetum lucidum.
- UV Absorption: The tapetum lucidum, located behind the retina, contains melanin, a pigment that absorbs UV rays. This absorption prevents harmful UV radiation from reaching the delicate retinal cells, protecting them from damage.
- Reduced Risk of Cataracts: UV radiation exposure is a known risk factor for cataract development. The protective filter in dogs' eyes reduces their exposure to UV rays, lowering the likelihood of cataracts and maintaining eye health.
- Long-Term Eye Health: Consistent protection from UV rays throughout a dog's life contributes to their overall eye health and well-being. This protection helps prevent age-related eye conditions and ensures optimal vision.
- Behavioral Implications: Dogs rely heavily on their vision for navigation, hunting, and social interactions. Protection from UV rays helps maintain their visual acuity and prevents discomfort or pain that could affect their behavior.
In summary, the protection from UV rays provided by the "how dogs see the world filter" is essential for maintaining eye health, preventing long-term damage, and ensuring optimal vision throughout a dog's life. This protection contributes to their overall well-being and allows them to fully engage with their environment.
Read also:Addison Vodka Insta A Comprehensive Guide To The Viral Sensation
Increased Light Sensitivity
Increased light sensitivity, a key component of the "how dogs see the world filter," refers to the enhanced ability of dogs to detect and utilize even faint sources of light, allowing them to perceive their surroundings effectively in low-light conditions.
- Enhanced Vision in Dim Environments: Dogs' increased light sensitivity allows them to navigate and interact with their environment effectively, even in low-light conditions such as twilight or dawn.
- Improved Depth Perception: The increased light sensitivity contributes to a dog's depth perception, enabling them to better gauge distances and avoid obstacles, even in low-light situations.
- Enhanced Motion Detection: The increased light sensitivity and improved depth perception work together to enhance a dog's ability to detect and track moving objects in low-light conditions.
- Hunting and Predation: Increased light sensitivity is particularly advantageous for dogs that hunt at dawn or dusk, allowing them to locate and pursue prey more effectively.
In summary, the increased light sensitivity component of the "how dogs see the world filter" empowers dogs to navigate, hunt, and interact with their environment effectively in low-light conditions, highlighting the remarkable adaptations that contribute to their unique sensory experiences.
Improved Depth Perception
Improved depth perception, as a component of the "how dogs see the world filter," plays a vital role in shaping the visual experiences of dogs. This enhanced ability to perceive depth and spatial relationships stems from the unique anatomical features of their eyes and visual processing mechanisms.
One key factor contributing to dogs' improved depth perception is their binocular vision, which involves the use of both eyes to create a single, three-dimensional image of the world. This allows dogs to accurately gauge distances and perceive the relative depth of objects in their environment. Additionally, the presence of a specialized region in the brain called the visual cortex, which is responsible for processing visual information, enables dogs to interpret depth cues and create a cohesive representation of the visual world.
The practical significance of improved depth perception for dogs is evident in various aspects of their behavior and survival. For instance, it aids in navigation, allowing dogs to move through their environment safely and efficiently. Depth perception is also crucial for hunting, as it helps dogs accurately judge the distance to their prey and plan their movements accordingly.
Furthermore, improved depth perception contributes to a dog's overall quality of life. It enables them to interact confidently with their surroundings, engage in play and social activities, and avoid potential hazards.
Motion Detection
Motion detection is a crucial aspect of the "how dogs see the world filter," enabling dogs to perceive and respond to moving objects with remarkable accuracy and efficiency. This ability stems from the unique anatomical features of their eyes and specialized neural mechanisms.
- Enhanced Visual Acuity: Dogs possess a higher concentration of cone cells in their retinas compared to humans, which contributes to their sharp visual acuity. This allows them to detect and track moving objects with greater precision.
- Peripheral Vision: Dogs have a wider field of view compared to humans, with a visual range of approximately 250 degrees. This wide peripheral vision enhances their ability to detect motion in their surroundings, even from the corners of their eyes.
- Specialized Neural Pathways: Dogs' brains have specialized neural pathways dedicated to motion detection. These pathways allow them to process visual information rapidly and respond to moving objects quickly.
- Survival and Hunting: Motion detection is vital for dogs' survival in the wild. It helps them detect potential predators, locate prey, and navigate their environment safely.
In conclusion, motion detection is an integral part of the "how dogs see the world filter." It empowers dogs to navigate their surroundings effectively, hunt successfully, and interact with their environment with confidence and precision.
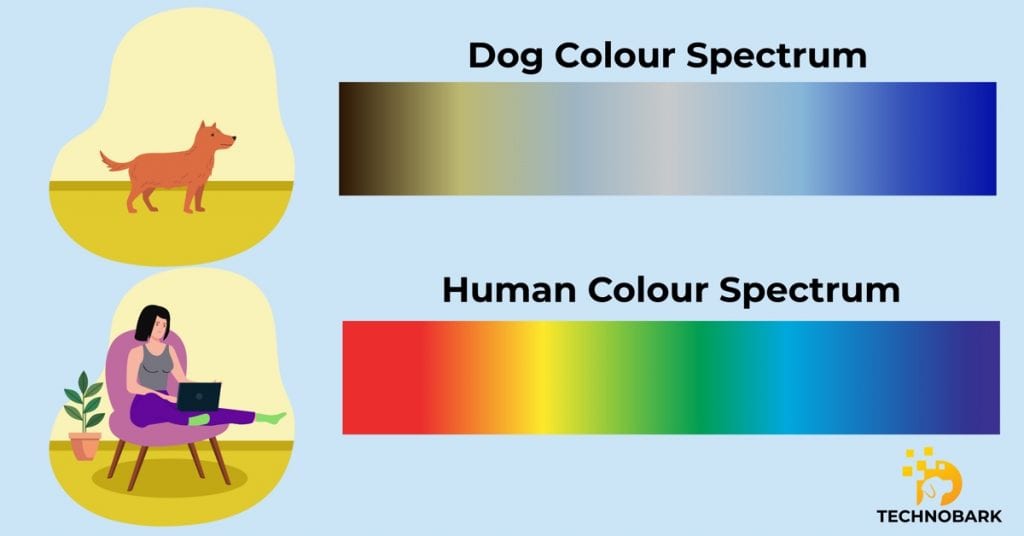
Color Perception
Within the intricate tapestry of "how dogs see the world filter," color perception plays a significant role in shaping their visual experiences. Unlike humans who possess trichromatic vision, dogs are dichromats, meaning they have only two types of cone cells in their retinas, primarily sensitive to blue and yellow wavelengths. This unique color perception system influences how dogs perceive and interact with their surroundings.
One notable consequence of dichromacy is that dogs have limited discrimination between red and green colors. What may appear vibrant red to us might be perceived as a shade of yellow or brown to a dog. This difference in color perception can affect various aspects of a dog's life, such as their ability to distinguish between ripe and unripe fruits or identify certain types of prey.
Despite their limited color perception compared to humans, dogs possess remarkable visual adaptations that enhance their survival and functionality. Their high concentration of rod cells, sensitive to low light conditions, grants them exceptional night vision. Additionally, their wide field of view and keen motion detection abilities compensate for their reduced color discrimination.
Understanding the connection between color perception and "how dogs see the world filter" is crucial for dog owners and trainers. By recognizing the limitations and strengths of canine color perception, we can better cater to their needs and create a more enriching environment for them. Whether it's choosing appropriate toys or training aids, considering their color perception can enhance their overall well-being and quality of life.
Visual Field of View
The visual field of view, a crucial component of "how dogs see the world filter," refers to the extent of the visible world that an individual can perceive at any given moment. In dogs, the visual field of view is significantly wider compared to humans, spanning approximately 250 degrees, with a nearly 180-degree binocular field. This panoramic vision grants dogs an evolutionary advantage in various aspects of their behavior and survival.
One significant implication of the wide visual field of view in dogs is enhanced peripheral vision. Unlike humans, who have a more narrow forward-facing visual field, dogs can detect movement and objects in their surroundings almost all around them. This panoramic view is particularly advantageous for detecting potential predators, locating prey, and navigating through dense vegetation or challenging terrain.
Moreover, the wide visual field of view contributes to dogs' depth perception and spatial awareness. The binocular overlap in their visual field allows them to accurately gauge distances and perceive the relative depth of objects in their environment. This depth perception is essential for activities such as hunting, chasing, and safely navigating uneven surfaces.
Understanding the connection between "Visual Field of View" and "how dogs see the world filter" is crucial for dog owners and trainers. By recognizing the importance of a wide visual field for a dog's perception and behavior, we can create training programs and provide enrichment activities that cater to their unique visual capabilities. This understanding also highlights the need for responsible dog ownership, ensuring that dogs have ample opportunities to explore and engage with their surroundings, fulfilling their natural instincts and enhancing their overall well-being.
Binocular Vision
Binocular vision, an essential component of "how dogs see the world filter," refers to the ability to use both eyes simultaneously to create a single, three-dimensional image of the world. This remarkable visual capability plays a vital role in shaping a dog's perception and interaction with its surroundings.
The binocular field of vision in dogs overlaps significantly, providing them with depth perception and an enhanced ability to accurately gauge distances and the relative positions of objects. This depth perception is crucial for a range of activities, including hunting, chasing prey, and navigating complex terrain. For instance, when a dog is tracking a moving object, the binocular vision allows it to precisely calculate the object's trajectory and adjust its pursuit accordingly.
Moreover, binocular vision contributes to a dog's ability to perceive spatial relationships and judge the size and shape of objects. This visual information is essential for successful social interactions, as it enables dogs to recognize and differentiate between familiar individuals and strangers. Additionally, binocular vision enhances a dog's ability to detect and avoid obstacles in its path, ensuring safe and efficient navigation through its environment.
Understanding the connection between binocular vision and "how dogs see the world filter" is crucial for responsible dog ownership and training. By recognizing the importance of binocular vision for a dog's perception and behavior, we can create training programs and provide enrichment activities that cater to their unique visual capabilities. This understanding also highlights the need for proper veterinary care to address any potential vision impairments that may impact a dog's quality of life.
Accommodation
Accommodation, a crucial aspect of "how dogs see the world filter," refers to the ability of the eye to adjust its focus to clearly perceive objects at varying distances. This dynamic visual capability enables dogs to swiftly and effectively adapt to their surroundings, from near to far.
- Dynamic Lens Adjustment: Dogs' lenses are highly flexible, allowing them to change shape to accommodate different focal lengths. This enables them to focus on objects both near and far without significant effort or delay.
- Clear Visual Perception: Accommodation ensures that light rays entering the eye converge precisely on the retina, resulting in a clear and focused image. This clarity is essential for dogs to accurately perceive their environment and respond appropriately.
- Hunting and Predation: Accommodation plays a vital role in a dog's ability to hunt and capture prey. It allows them to quickly adjust their focus from distant moving objects to the close-up details of their target, enhancing their accuracy and success.
- Depth Perception and Spatial Awareness: Accommodation contributes to depth perception and spatial awareness by providing clear visual information about the relative distances of objects in the environment. This enables dogs to navigate their surroundings safely and interact with objects appropriately.
In summary, accommodation is a fundamental component of "how dogs see the world filter." It empowers dogs with dynamic visual capabilities, allowing them to perceive their environment clearly at varying distances. This ability is essential for hunting, navigation, and overall interaction with the world around them.
Tear Production
Tear production, an integral component of "how dogs see the world filter," plays a multifaceted role in maintaining ocular health and visual clarity. These tears, primarily composed of water, electrolytes, and proteins, serve several essential functions that directly impact a dog's ability to perceive and interact with its surroundings.
Firstly, tear production helps to lubricate the surface of the eye, preventing dryness and irritation. This lubrication is crucial for maintaining corneal transparency, which is essential for clear vision. Without adequate tear production, the cornea can become cloudy or damaged, leading to impaired vision or even blindness.
Moreover, tears contain antimicrobial substances that protect the eye from infections. They wash away foreign particles, such as dust or debris, and create a hostile environment for bacteria and viruses. This protective function ensures that the delicate structures of the eye remain healthy and free from infection, safeguarding a dog's vision.
In summary, tear production is an indispensable component of "how dogs see the world filter." It maintains ocular health, prevents dryness and irritation, and protects against infections, all of which are essential for clear vision and the overall well-being of a dog.
FAQs
This section addresses commonly asked questions and misconceptions regarding "how dogs see the world filter," providing informative answers based on scientific research and expert knowledge.
Question 1: Do dogs see the world in black and white?
Answer: No, dogs are not completely color-blind. While they have dichromatic vision and lack the same range of color perception as humans, they can still distinguish between certain colors, primarily blue and yellow.
Question 2: Why do dogs have a "filter" over their eyes?
Answer: The "filter" referred to is the tapetum lucidum, a reflective layer located behind the retina. It enhances dogs' vision in low-light conditions by reflecting light back into the eye, increasing the amount of light available to photoreceptors.
Question 3: Do dogs have better night vision than humans?
Answer: Yes, dogs generally have better night vision than humans due to the presence of the tapetum lucidum. This adaptation allows them to see in dim light, making them well-suited for hunting and navigating in low-light environments.
Question 4: Can dogs see better than humans during the day?
Answer: No, dogs do not have better vision than humans during the day. Human vision is characterized by higher visual acuity, allowing for sharper and more detailed perception, particularly in well-lit conditions.
Question 5: Do all dogs have the same type of vision?
Answer: No, there can be variations in vision among different dog breeds. Some breeds may have inherited traits or adaptations that influence their visual capabilities, such as enhanced night vision or sensitivity to certain colors.
Question 6: How can I protect my dog's vision?
Answer: Regular veterinary check-ups are crucial for monitoring your dog's eye health. Additionally, providing a balanced diet, avoiding exposure to harmful substances, and offering appropriate eye protection during outdoor activities can help maintain their vision.
In conclusion, understanding "how dogs see the world filter" provides valuable insights into our canine companions' unique visual experiences. By addressing common questions and dispelling misconceptions, we can appreciate the remarkable adaptations that enable dogs to perceive and interact with their surroundings.
Transition to the next article section:
Tips to Enhance Dog Vision
Understanding "how dogs see the world filter" can inform practical tips to support their visual well-being. By considering their unique visual capabilities, we can create environments and provide care that optimizes their ability to perceive and interact with the world around them.
Tip 1: Respect Their Limited Color Vision: Dogs have dichromatic vision, meaning they primarily see shades of blue and yellow. When choosing toys or training aids, opt for colors within this spectrum for better visibility.
Tip 2: Provide Ample Lighting: Dogs rely on light reflection for clear vision, especially in low-light conditions. Ensure their living spaces are well-lit to enhance their mobility and prevent them from bumping into objects.
Tip 3: Avoid Sudden Movements: Dogs' wide field of view makes them sensitive to sudden movements. When approaching them, do so calmly and gradually to prevent startling them.
Tip 4: Protect Their Eyes Outdoors: Exposure to bright sunlight can damage a dog's eyes. Provide them with sunglasses or visors designed for dogs when engaging in outdoor activities.
Tip 5: Maintain a Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in antioxidants and vitamins A and E supports overall eye health and prevents vision-related issues.
Tip 6: Schedule Regular Vet Check-Ups: Regular veterinary eye examinations can detect and address any underlying eye conditions or diseases that may affect your dog's vision.
Tip 7: Create Safe Environments: Ensure your dog's surroundings are free from potential eye hazards, such as sharp objects or toxic substances that could cause injury or irritation.
Tip 8: Consider Breed-Specific Visual Needs: Different dog breeds may have varying visual capabilities. Research your dog's breed to understand any inherited traits or special considerations related to their vision.
By incorporating these tips into your dog's care routine, you can provide a supportive environment that caters to their unique visual needs. Remember, understanding "how dogs see the world filter" empowers us to be responsible and informed guardians, enhancing the quality of life for our canine companions.
Transition to the article's conclusion:
Conclusion
Our exploration of "how dogs see the world filter" unveils the remarkable adaptations that shape canine visual experiences. Their unique visual capabilities, including enhanced night vision, improved depth perception, and a wider field of view, provide them with distinct advantages in their environment. Understanding these adaptations enables us to appreciate the complexities of their perception and tailor our interactions and care accordingly.
As responsible dog owners and enthusiasts, it is crucial to recognize and respect the unique visual world of our canine companions. By considering their limited color vision, providing ample lighting, and safeguarding their eyes from potential hazards, we can create environments that support their visual well-being. Additionally, embracing their keen motion detection and depth perception through engaging activities and training exercises can enhance their overall quality of life.
The "how dogs see the world filter" serves as a reminder of the fascinating diversity of sensory perception in the animal kingdom. As we continue to unravel the intricate workings of canine vision, we gain a deeper appreciation for the unique perspectives and experiences of our beloved dogs.