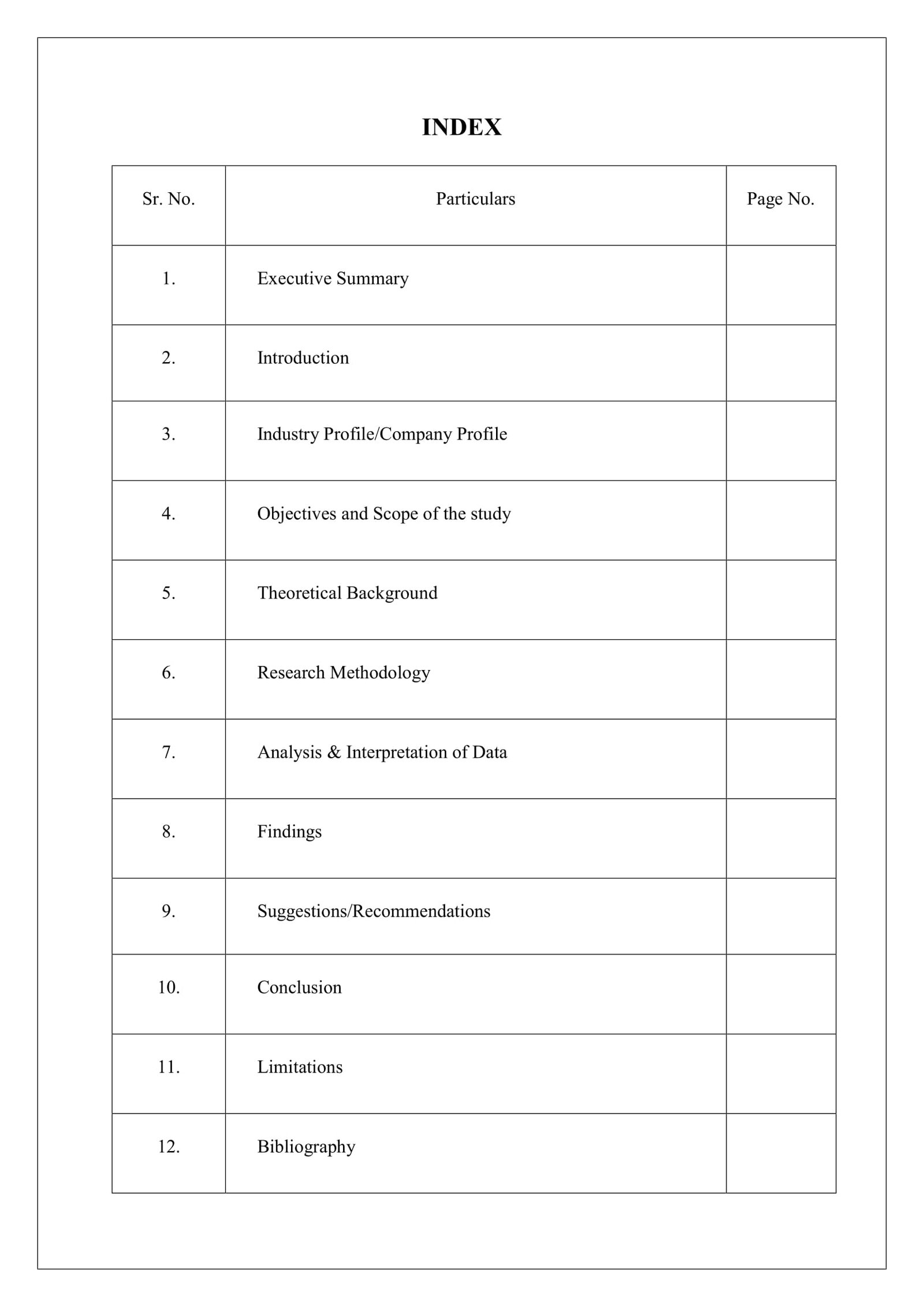
An index is a systematic list of items, usually arranged alphabetically or numerically, that provides a quick and easy way to locate information in a larger work, such as a book, database, or website. For example, an index of a book might list the page numbers where each chapter begins, while an index of a database might list the fields and records that are included.
Indexes are essential for navigating large amounts of information, and they can save a great deal of time when you are looking for something specific. They are also important for ensuring that information is organized and easy to find, which can be crucial in fields such as research and law.
The history of indexing dates back to the ancient world, when scholars would create indexes of scrolls and books to help them find information more easily. Today, indexes are used in a wide variety of applications, from libraries and archives to online databases and websites.
Read also:Robert Palmers Son Death Unveiling The Tragic Story Behind The Headlines
Index
An index is a systematic list of items, usually arranged alphabetically or numerically, that provides a quick and easy way to locate information in a larger work, such as a book, database, or website. Indexes are essential for navigating large amounts of information, and they can save a great deal of time when you are looking for something specific.
- Organization: Indexes help to organize information in a logical and consistent way, making it easier to find what you are looking for.
- Navigation: Indexes provide a quick and easy way to navigate large amounts of information, such as a book or database.
- Research: Indexes are essential for research, as they allow you to quickly and easily find information on a specific topic.
- Accuracy: Indexes are an accurate way to find information, as they are typically created by experts in the field.
- Efficiency: Indexes can save you a great deal of time when you are looking for something specific, as they allow you to quickly and easily find the information you need.
- Comprehensiveness: Indexes are typically comprehensive, meaning that they include all of the information that is available on a specific topic.
- Accessibility: Indexes are accessible to everyone, regardless of their level of education or expertise.
- Historical: Indexes have been used for centuries to organize and navigate information.
These are just a few of the key aspects of indexes. They are an essential tool for anyone who needs to find information quickly and easily.
Organization
An index is a systematic list of items, usually arranged alphabetically or numerically, that provides a quick and easy way to locate information in a larger work, such as a book, database, or website. Indexes are essential for navigating large amounts of information, and they can save a great deal of time when you are looking for something specific.
- Structure
An index is typically organized in a hierarchical structure, with broader topics divided into narrower subtopics. This makes it easy to find the information you are looking for, even if you don't know exactly where it is located. - Consistency
Indexes are created using consistent rules and standards, which ensures that they are easy to use and understand. This consistency makes it easy to find information in any index, regardless of who created it. - Accuracy
Indexes are typically created by experts in the field, which ensures that they are accurate and reliable. This accuracy is essential for research and other tasks where it is important to find accurate information. - Comprehensiveness
Indexes are typically comprehensive, meaning that they include all of the information that is available on a specific topic. This comprehensiveness makes indexes an essential tool for researchers and other professionals who need to find all of the information on a specific topic.
The organization of indexes makes them an essential tool for anyone who needs to find information quickly and easily. By providing a structured, consistent, accurate, and comprehensive way to organize information, indexes make it possible to find the information you need when you need it.
Navigation
An index is a systematic list of items, usually arranged alphabetically or numerically, that provides a quick and easy way to locate information in a larger work, such as a book, database, or website. Indexes are essential for navigating large amounts of information, and they can save a great deal of time when you are looking for something specific.
- Ease of Use
One of the key benefits of indexes is that they are easy to use. They are typically organized in a logical and consistent way, making it easy to find the information you are looking for. Additionally, indexes are typically created using standard formats and conventions, which makes them familiar and easy to use for anyone who has used an index before.
Read also:
- Addison Vodka Insta A Comprehensive Guide To The Viral Sensation
- Speed
Indexes can also save you a great deal of time when you are looking for something specific. This is because indexes provide a quick and direct way to find the information you need, without having to search through the entire document.
- Accuracy
Indexes are typically created by experts in the field, which ensures that they are accurate and reliable. This accuracy is essential for research and other tasks where it is important to find accurate information.
- Comprehensiveness
Indexes are typically comprehensive, meaning that they include all of the information that is available on a specific topic. This comprehensiveness makes indexes an essential tool for researchers and other professionals who need to find all of the information on a specific topic.
These are just a few of the key benefits of indexes. They are an essential tool for anyone who needs to navigate large amounts of information quickly and easily.
Research
An index is a systematic list of items, usually arranged alphabetically or numerically, that provides a quick and easy way to locate information in a larger work, such as a book, database, or website. Indexes are essential for research, as they allow you to quickly and easily find information on a specific topic.
- Organization
Indexes are organized in a logical and consistent way, making it easy to find the information you are looking for. This is especially important for researchers, who often need to find information on a specific topic quickly and easily.
- Comprehensiveness
Indexes are typically comprehensive, meaning that they include all of the information that is available on a specific topic. This makes them an essential tool for researchers, who need to be able to find all of the information on a specific topic in order to conduct their research.
- Accuracy
Indexes are typically created by experts in the field, which ensures that they are accurate and reliable. This is essential for researchers, who need to be able to trust the information they are using in their research.
- Time-saving
Indexes can save researchers a great deal of time. By providing a quick and easy way to find information on a specific topic, indexes can help researchers to conduct their research more efficiently.
These are just a few of the reasons why indexes are essential for research. By providing a quick and easy way to find information on a specific topic, indexes can help researchers to conduct their research more efficiently and effectively.
Accuracy
The accuracy of indexes is a crucial aspect that sets them apart as a reliable tool for finding information. Since indexes are typically created by experts in the field, they undergo a rigorous process of research and verification to ensure their accuracy. This meticulous approach guarantees that the information provided in indexes is trustworthy and dependable.
- Subject Matter Expertise
Experts in the field possess a deep understanding of the subject matter they index. Their knowledge and experience enable them to create indexes that are comprehensive, accurate, and reflect the latest developments in their respective domains.
- Rigorous Research
The creation of indexes involves thorough research and fact-checking. Experts consult multiple sources, including scholarly articles, books, and databases, to ensure the accuracy of the information included in the index.
- Standardized Processes
Indexes are often created following standardized processes and guidelines. These standards help ensure consistency, accuracy, and completeness across different indexes, making it easier for users to find the information they need.
- Peer Review
In many cases, indexes undergo peer review by other experts in the field. This process involves scrutinizing the index for accuracy, completeness, and adherence to established standards.
The accuracy of indexes is paramount for researchers, students, and professionals who rely on them to find trustworthy and up-to-date information. The involvement of experts in the field, coupled with rigorous research and standardized processes, ensures that indexes remain a valuable tool for accessing accurate and reliable information.
Efficiency
Indexes are an invaluable tool for saving time when searching for specific information within a larger body of work. By providing a systematic and organized listing of keywords, concepts, or topics, indexes allow users to bypass the need to read through an entire document, saving significant time and effort.
The efficiency of indexes is particularly apparent in research and academic settings, where vast amounts of information need to be processed and analyzed. For example, a researcher using an index to locate specific studies or data points within a comprehensive academic database can significantly reduce the time spent searching through irrelevant material.
In the context of digital libraries and online repositories, indexes play a crucial role in enhancing user experience. By allowing users to quickly and easily narrow down their search results, indexes improve the overall accessibility and usability of these resources.
Furthermore, the efficiency of indexes extends to other areas such as legal documentation, technical manuals, and historical archives. By providing a structured and organized approach to finding information, indexes empower users to access the knowledge they need quickly and effectively.
In conclusion, the efficiency of indexes is a key component of their value and utility. By enabling users to quickly and easily find the information they need, indexes save time, improve productivity, and enhance the overall accessibility of knowledge.
Comprehensiveness
The comprehensiveness of indexes is a defining characteristic that sets them apart as a valuable tool for research and information retrieval. Indexes strive to provide a complete and exhaustive listing of all relevant information on a specific topic, ensuring that users can locate the resources they need with confidence.
- Breadth of Coverage
Indexes aim to cover a broad range of sources, including books, articles, journals, websites, and other relevant materials. By incorporating information from multiple sources, indexes provide a comprehensive view of the available knowledge on a topic. - Depth of Detail
Indexes provide detailed information about each entry, including bibliographic data, abstracts, and sometimes even full-text content. This depth of detail allows users to quickly assess the relevance of each entry and make informed decisions about which resources to consult. - Currency and Timeliness
Indexes are regularly updated to include the latest information on a topic. This ensures that users have access to the most current and up-to-date resources, enabling them to stay informed about the latest developments in their field of interest. - Accuracy and Reliability
The accuracy and reliability of indexes are crucial for their usefulness. Indexes are typically compiled by experts in the field, who carefully review and verify the information included to ensure its accuracy and credibility.
The comprehensiveness of indexes is essential for researchers, students, and professionals who need to access complete and up-to-date information on a specific topic. By providing a comprehensive listing of relevant resources, indexes empower users to conduct thorough research, make informed decisions, and stay abreast of the latest knowledge in their field.
Accessibility
In the realm of information retrieval, accessibility is paramount. Indexes play a crucial role in making information accessible to everyone, irrespective of their educational background or level of expertise. Their user-friendly nature and structured organization empower individuals to navigate vast bodies of knowledge effortlessly.
- Simplicity and Clarity
Indexes are designed with simplicity and clarity in mind. They employ straightforward language and intuitive arrangements, enabling users to grasp the structure and content quickly. This user-centric approach ensures that individuals with diverse backgrounds can access and comprehend the information presented. - Standardized Formats
Indexes adhere to standardized formats and conventions, providing a consistent framework for users. The predictable layout and organization allow individuals to navigate different indexes seamlessly, regardless of their familiarity with a particular subject or resource. - Multiple Access Points
Indexes offer multiple access points to accommodate diverse search preferences. They may be organized alphabetically, chronologically, or by subject, providing users with flexibility in finding the information they seek. This multifaceted approach caters to different learning styles and research strategies. - Technological Advancements
Technological advancements have further enhanced the accessibility of indexes. Digital indexes and online databases allow users to access information remotely and with greater ease. User-friendly interfaces and advanced search functionalities empower individuals to refine their searches and locate specific content efficiently.
The accessibility of indexes is not merely a convenience but a fundamental principle that promotes inclusivity and knowledge dissemination. By breaking down barriers to information, indexes empower individuals to engage in lifelong learning, research, and personal growth.
Historical
Throughout history, indexes have played a pivotal role in organizing and navigating vast amounts of information, serving as indispensable tools for scholars, researchers, and individuals seeking knowledge. Their enduring presence across centuries underscores their fundamental importance in accessing, comprehending, and disseminating information.
- Ancient Origins
The origins of indexes can be traced back to ancient civilizations. In the libraries of Alexandria and Pergamon, scholars devised rudimentary indexes to catalog scrolls and facilitate research. These early indexes consisted of simple lists and may have included annotations or summaries of the contents.
- Medieval Advancements
During the Middle Ages, indexes became more sophisticated as the volume of written knowledge grew. Monastic scribes developed elaborate indexes for religious texts, such as the Bible and commentaries, to aid in the study and interpretation of complex theological concepts.
- Renaissance and Scientific Revolution
The Renaissance and Scientific Revolution witnessed a surge in the production of books and scientific treatises. Indexes played a crucial role in organizing and accessing this rapidly expanding body of knowledge. Prominent scholars, including Francis Bacon and Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz, advocated for the use of indexes as essential tools for scientific inquiry and intellectual advancement.
- Modern Developments
In the modern era, indexes have evolved alongside technological advancements. The advent of computers and digital databases has enabled the creation of vast, searchable indexes that encompass a wide range of information sources, from academic journals to online resources.
The historical significance of indexes underscores their enduring value in managing and accessing information. From ancient libraries to modern digital repositories, indexes have consistently served as gateways to knowledge, empowering individuals to explore, understand, and build upon the accumulated wisdom of humanity.
Frequently Asked Questions about Indexes
Indexes are an essential tool for navigating large amounts of information, such as books, databases, and websites. They can save you time and help you find the information you need quickly and easily. Here are some frequently asked questions about indexes:
Question 1: What is an index?
An index is a systematic list of items, usually arranged alphabetically or numerically, that provides a quick and easy way to locate information in a larger work.
Question 2: What are the benefits of using an index?
Indexes can save you time, help you find the information you need quickly and easily, and provide a comprehensive overview of the contents of a larger work.
Question 3: How do I use an index?
To use an index, simply look up the topic or keyword you are interested in. The index will provide you with a list of page numbers where you can find more information on that topic.
Question 4: What are some examples of indexes?
Indexes can be found in a variety of sources, including books, databases, websites, and even printed materials such as magazines and newspapers.
Question 5: How can I create an index?
There are a variety of software programs that can help you create an index. You can also create an index manually, but this can be a time-consuming process.
Question 6: What are some tips for using indexes effectively?
When using an index, it is important to be specific in your search terms. You should also use keywords and synonyms to find all of the relevant information.
Indexes are a valuable tool for anyone who needs to find information quickly and easily. By understanding how to use indexes effectively, you can save time and improve your research skills.
Transition to the next article section...
Index Usage Tips
Indexes are invaluable research tools that enable efficient navigation of vast information sources. By employing effective indexing techniques, you can optimize your search process and maximize your research outcomes.
Tip 1: Utilize Specific Search TermsWhen searching an index, employ precise and specific keywords related to your topic. This approach enhances the relevance of search results and minimizes irrelevant information.Tip 2: Leverage Keywords and Synonyms
Expand your search by incorporating synonyms and alternative keywords associated with your topic. This comprehensive approach ensures that you capture all pertinent information, even if expressed using different terminology.Tip 3: Pay Attention to Context
Consider the context of your search terms within the larger work. Understanding the surrounding information helps refine your search and leads to more accurate results.Tip 4: Utilize Multiple Indexes
Consult multiple indexes to increase the comprehensiveness of your search. Different indexes may provide complementary information, offering a broader perspective on your topic.Tip 5: Evaluate Index Quality
Assess the quality of the index before relying on its results. Consider factors such as its comprehensiveness, accuracy, and currency to ensure the reliability of the information you obtain.
By incorporating these tips into your indexing practices, you can harness the full potential of indexes and significantly enhance your research efficiency and effectiveness.
Key Takeaways:
- Specificity and precision in search terms yield more relevant results.
- Employing synonyms and alternative keywords expands search coverage.
- Understanding the context of search terms improves accuracy.
- Consulting multiple indexes provides a comprehensive perspective.
- Evaluating index quality ensures the reliability of search results.
Conclusion:
Mastering the art of effective index usage empowers researchers with the ability to navigate vast information landscapes with precision and efficiency. By adhering to these practical tips, you can unlock the full potential of indexes and elevate your research endeavors to new heights.Conclusion
An index serves as an indispensable tool for navigating vast information repositories, providing a systematic and organized approach to locate specific content. Its comprehensive coverage, coupled with its accuracy and efficiency, makes it an invaluable asset for researchers, students, and professionals alike.
By understanding the significance of indexing and adopting effective usage techniques, individuals can harness the full potential of this powerful research aid. Indexes empower users to navigate complex information landscapes with precision, enabling them to uncover insights and knowledge that would otherwise remain hidden. As the volume of information continues to grow at an unprecedented pace, the mastery of indexing skills becomes increasingly critical for successful research and lifelong learning.