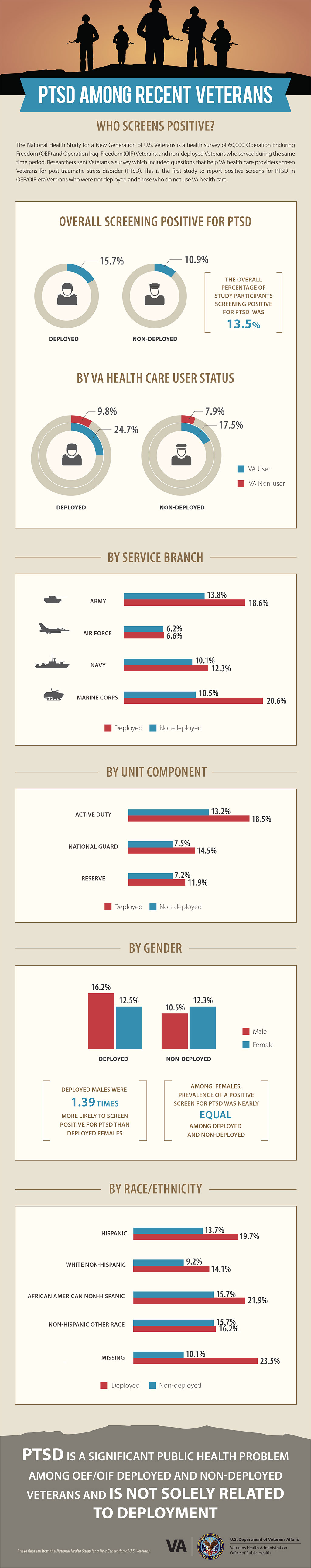
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a mental health condition that can occur in people who have experienced or witnessed a traumatic event. Symptoms of PTSD can include flashbacks, nightmares, avoidance of reminders of the trauma, and difficulty sleeping. PTSD can be caused by a variety of traumatic events, including combat exposure, sexual assault, and natural disasters.
PTSD is a serious mental health condition that can have a significant impact on a person's life. It is important to seek professional help if you think you may be experiencing PTSD. Treatment for PTSD typically involves psychotherapy and/or medication.
There are a number of resources available to help people with PTSD. The National Center for PTSD offers a variety of resources, including information on PTSD, treatment options, and support groups. The Veterans Administration also offers a number of resources for veterans with PTSD.
Read also:The Third Place Global Eatery Clovis Menu
PTSD Like I Came From Iraq
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a mental health condition that can occur in people who have experienced or witnessed a traumatic event. PTSD can be caused by a variety of traumatic events, including combat exposure, sexual assault, and natural disasters.
- Symptoms
- Causes
- Diagnosis
- Treatment
- Prognosis
- Prevention
- Epidemiology
- History
- Society and culture
PTSD is a serious mental health condition that can have a significant impact on a person's life. It is important to seek professional help if you think you may be experiencing PTSD. Treatment for PTSD typically involves psychotherapy and/or medication.
There are a number of resources available to help people with PTSD. The National Center for PTSD offers a variety of resources, including information on PTSD, treatment options, and support groups. The Veterans Administration also offers a number of resources for veterans with PTSD.
Symptoms
The symptoms of PTSD can vary depending on the individual and the severity of the trauma they have experienced. However, some of the most common symptoms include:
- Flashbacks
- Nightmares
- Avoidance of reminders of the trauma
- Difficulty sleeping
- Irritability
- Anger
- Guilt
- Shame
- Difficulty concentrating
- Difficulty making decisions
- Physical symptoms, such as headaches, stomachaches, and fatigue
PTSD can have a significant impact on a person's life. It can make it difficult to work, go to school, and maintain relationships. PTSD can also lead to depression, anxiety, and other mental health problems.
If you think you may be experiencing PTSD, it is important to seek professional help. Treatment for PTSD can help you manage your symptoms and improve your quality of life.
Read also:Has Cooper Alan Won Any Awards Unveiling The Achievements Of A Rising Star
Causes
PTSD can be caused by a variety of traumatic events, including combat exposure, sexual assault, and natural disasters. In the case of "ptsd like i came from iraq," the trauma is likely to be related to combat exposure.
Combat exposure is a well-known risk factor for PTSD. Soldiers who have been exposed to combat are at an increased risk of developing PTSD, even if they were not directly injured or killed. The risk of PTSD is even higher for soldiers who have been exposed to multiple traumatic events, such as combat deaths or injuries.
There are a number of factors that can contribute to the development of PTSD after combat exposure. These factors include the severity of the trauma, the duration of the trauma, and the soldier's individual resilience. Soldiers who are more resilient are less likely to develop PTSD, even after exposure to severe trauma.
Understanding the causes of PTSD is important for developing effective prevention and treatment strategies. By understanding the risk factors for PTSD, we can take steps to reduce the risk of developing PTSD in soldiers and other individuals who are at risk.
Diagnosis
PTSD can be diagnosed by a mental health professional, such as a psychiatrist or psychologist. The diagnosis is based on a clinical interview and a review of the person's symptoms. The clinician will ask about the person's experiences, including any traumatic events they have witnessed or experienced. The clinician will also ask about the person's symptoms, such as flashbacks, nightmares, and avoidance of reminders of the trauma.
In the case of "ptsd like i came from iraq," the diagnosis is likely to be based on the person's experiences in combat. The clinician will ask about the person's exposure to combat, including any traumatic events they witnessed or experienced. The clinician will also ask about the person's symptoms, such as flashbacks, nightmares, and avoidance of reminders of combat.
Diagnosis is important for PTSD because it allows the person to access treatment. Treatment can help people manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life.
Treatment
PTSD is a serious mental health condition that can have a significant impact on a person's life. However, there are a number of effective treatments available for PTSD, including psychotherapy, medication, and self-help strategies.
- Psychotherapy
Psychotherapy is a type of talk therapy that can help people with PTSD understand their symptoms and develop coping mechanisms. There are a number of different types of psychotherapy that can be effective for PTSD, including cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), exposure therapy, and eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR).
- Medication
Medication can also be helpful in treating PTSD. There are a number of different types of medication that can be used for PTSD, including antidepressants, anti-anxiety medications, and mood stabilizers.
- Self-help strategies
There are a number of self-help strategies that can help people with PTSD manage their symptoms. These strategies include exercise, relaxation techniques, and social support.
The best treatment for PTSD will vary depending on the individual. It is important to work with a mental health professional to develop a treatment plan that is right for you.
Prognosis
Prognosis for PTSD varies depending on a number of factors, including the severity of the trauma, the individual's resilience, and the availability of treatment. However, research suggests that with proper treatment, most people with PTSD can improve their symptoms and quality of life.
- Severity of the trauma
The severity of the trauma is a major factor in determining the prognosis for PTSD. People who have experienced more severe trauma are more likely to develop PTSD and to have more severe symptoms. However, even people who have experienced severe trauma can recover with proper treatment.
- Individual resilience
Individual resilience is another important factor in determining the prognosis for PTSD. People who are more resilient are more likely to recover from PTSD, even after exposure to severe trauma. Resilience can be built through a variety of factors, including social support, coping skills, and a positive outlook on life.
- Availability of treatment
The availability of treatment is also a critical factor in determining the prognosis for PTSD. People who have access to treatment are more likely to recover from PTSD and to have a better quality of life. However, treatment for PTSD is not always available, especially in low-resource settings.
Overall, the prognosis for PTSD is generally good with proper treatment. However, the severity of the trauma, the individual's resilience, and the availability of treatment all play a role in determining the outcome.
Prevention
Prevention is an important part of reducing the risk of developing PTSD, including "ptsd like i came from iraq". There are a number of things that can be done to prevent PTSD, including:
- Education
Educating people about PTSD and its risk factors can help to reduce the stigma associated with the condition and encourage people to seek help if they are experiencing symptoms. - Training
Training mental health professionals and other frontline workers to recognize and treat PTSD can help to ensure that people who are experiencing symptoms can get the help they need. - Social support
Providing social support to people who have experienced trauma can help to reduce their risk of developing PTSD. Social support can come from family, friends, community groups, or other sources. - Self-care
Practicing self-care can help to reduce stress and improve resilience, which can help to prevent PTSD. Self-care includes activities such as exercise, relaxation techniques, and getting enough sleep.
Preventing PTSD is not always possible, but there are a number of things that can be done to reduce the risk. By raising awareness of PTSD, training mental health professionals, providing social support, and promoting self-care, we can help to reduce the number of people who develop this debilitating condition.
Epidemiology
Epidemiology is the study of the distribution and determinants of health-related states or events (including disease), and the application of this study to the control of diseases and other health problems.
PTSD is a mental health condition that can occur in people who have experienced or witnessed a traumatic event. PTSD can be caused by a variety of traumatic events, including combat exposure, sexual assault, and natural disasters.
The epidemiology of PTSD is important for understanding the causes and risk factors for the condition, as well as for developing effective prevention and treatment strategies.
Research on the epidemiology of PTSD has found that the condition is relatively common, affecting approximately 6.8% of the US population at some point in their lives. PTSD is more common in women than in men, and it is more common in people who have experienced multiple traumas.
Risk factors for PTSD include a history of trauma, a family history of PTSD, and certain personality traits, such as neuroticism and introversion.
Understanding the epidemiology of PTSD can help us to better understand the condition and to develop more effective prevention and treatment strategies.
History
Historical trauma is a term used to describe the collective, cumulative, and enduring psychological trauma experienced by a group of people as a result of a history of oppression, violence, or discrimination. Historical trauma can be passed down through generations, and it can have a profound impact on the mental health of individuals and communities.
The concept of historical trauma is particularly relevant to understanding the experiences of people who have served in the military, especially those who have been deployed to war zones. War is a traumatic experience, and it can lead to the development of PTSD. In addition, veterans may also experience historical trauma as a result of their experiences with discrimination, racism, or other forms of oppression.
For example, a study of Vietnam veterans found that those who had experienced discrimination were more likely to develop PTSD. Another study found that African American veterans were more likely to experience PTSD than white veterans, even after controlling for combat exposure.
Understanding the connection between history and PTSD is important for developing effective prevention and treatment strategies. By understanding the historical factors that contribute to PTSD, we can better understand the needs of veterans and other populations who are at risk for developing this condition.
In addition, understanding the history of PTSD can help us to develop more effective ways to prevent this condition. For example, we can work to reduce discrimination and racism, and we can provide support to veterans and other populations who are at risk for developing PTSD.
Society and culture
Society and culture play a significant role in shaping the experiences of individuals with PTSD, including those who have served in the military and experienced combat-related trauma.
- Stigma and discrimination
Stigma and discrimination are major barriers to seeking help for PTSD. In many cultures, mental health issues are seen as a sign of weakness or shame. This can lead to individuals with PTSD feeling isolated and alone, and it can prevent them from seeking the help they need.
- Social support
Social support is essential for recovery from PTSD. Individuals with PTSD need to feel supported by their family, friends, and community. This support can help them to cope with the symptoms of PTSD and to rebuild their lives.
- Cultural beliefs and practices
Cultural beliefs and practices can influence the way that PTSD is experienced and treated. In some cultures, PTSD may be seen as a spiritual or religious issue, and treatment may involve traditional healing practices.
- Media representations
The media can play a role in shaping public perceptions of PTSD. Negative or inaccurate portrayals of PTSD in the media can contribute to stigma and discrimination. However, positive and accurate portrayals can help to increase awareness and understanding of PTSD.
It is important to understand the role that society and culture play in PTSD in order to develop effective prevention and treatment strategies. By addressing stigma and discrimination, providing social support, and promoting cultural sensitivity, we can create a more supportive environment for individuals with PTSD.
PTSD Like I Came From Iraq
This section addresses frequently asked questions and misconceptions about PTSD "like I came from Iraq".
Question 1: Is PTSD only experienced by military veterans?
Answer: No, PTSD can be experienced by anyone who has witnessed or experienced a traumatic event. While combat exposure is a common cause of PTSD, it is not the only cause.
Question 2: Are there different types of PTSD?
Answer: Yes, there are different types of PTSD, including acute PTSD, chronic PTSD, and complex PTSD. Acute PTSD lasts for less than 3 months, chronic PTSD lasts for 3 months or more, and complex PTSD is a more severe form of PTSD that is often caused by prolonged or repeated trauma.
Question 3: What are the symptoms of PTSD?
Answer: The symptoms of PTSD can vary, but they often include flashbacks, nightmares, avoidance of reminders of the trauma, difficulty sleeping, irritability, anger, guilt, shame, difficulty concentrating, difficulty making decisions, and physical symptoms, such as headaches, stomachaches, and fatigue.
Question 4: How is PTSD diagnosed?
Answer: PTSD is diagnosed by a mental health professional, such as a psychiatrist or psychologist. The diagnosis is based on a clinical interview and a review of the person's symptoms.
Question 5: How is PTSD treated?
Answer: PTSD is treated with a combination of psychotherapy, medication, and self-help strategies. Psychotherapy can help people with PTSD understand their symptoms and develop coping mechanisms. Medication can also be helpful in treating PTSD. Self-help strategies include exercise, relaxation techniques, and social support.
Question 6: Can PTSD be prevented?
Answer: PTSD cannot always be prevented, but there are things that can be done to reduce the risk of developing PTSD after exposure to a traumatic event. These things include education, training, social support, and self-care.
PTSD is a serious mental health condition, but it is important to remember that there is hope for recovery. With proper treatment, people with PTSD can manage their symptoms and live full and productive lives.
For more information on PTSD, please visit the National Center for PTSD website: https://www.ptsd.va.gov/
Move on to the next section: Understanding the Impact of PTSD
Tips for Managing PTSD "Like I Came From Iraq"
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a serious mental health condition that can occur after exposure to a traumatic event. PTSD can cause a wide range of symptoms, including flashbacks, nightmares, avoidance of reminders of the trauma, difficulty sleeping, irritability, anger, guilt, shame, difficulty concentrating, difficulty making decisions, and physical symptoms, such as headaches, stomachaches, and fatigue.
If you are experiencing symptoms of PTSD, it is important to seek professional help. Treatment can help you manage your symptoms and improve your quality of life.
In addition to professional treatment, there are a number of things you can do to help manage your PTSD symptoms. Here are five tips:
Tip 1: EducationEducate yourself about PTSD. This can help you to understand your symptoms and develop coping mechanisms.
Tip 2: Social supportConnect with other people who have PTSD. This can provide you with support and understanding.
Tip 3: Self-careTake care of yourself both physically and emotionally. This includes eating a healthy diet, getting enough sleep, and exercising regularly.
Tip 4: Relaxation techniquesLearn and practice relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing and meditation. These techniques can help to reduce stress and improve your sleep.
Tip 5: Avoid alcohol and drugsAlcohol and drugs can worsen PTSD symptoms. If you are struggling with substance abuse, seek professional help.
These are just a few tips for managing PTSD. If you are experiencing symptoms of PTSD, it is important to seek professional help. Treatment can help you manage your symptoms and improve your quality of life.
For more information on PTSD, please visit the National Center for PTSD website: https://www.ptsd.va.gov/
Move on to the next section: Understanding the Impact of PTSD
Conclusion
PTSD "like I came from Iraq" is a serious mental health condition that can have a significant impact on a person's life. It is important to understand the symptoms of PTSD and to seek professional help if you think you may be experiencing them.
With proper treatment, people with PTSD can manage their symptoms and live full and productive lives. However, there is still much that we do not know about PTSD. More research is needed to develop more effective treatments and to find ways to prevent PTSD from developing in the first place.
In the meantime, we can all do our part to support people with PTSD. We can educate ourselves about PTSD, we can provide social support to people who are struggling, and we can advocate for policies that support people with PTSD.
Together, we can make a difference in the lives of people with PTSD.